Introduction to Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Recycling
Hot rolled carbon steel is the most commonly used material, considering strength, versatility, and cost. Hot rolled carbon steel forms the backbone of a great number of structures and products found in construction, automotive, and industrial applications. All steel products have a life cycle. When that life cycle comes to an end, then the steel product is considered scrapped—that is, it is ready for recycling. In a circular economy, hot rolled carbon steel recycling reduces not only natural resource depletion but also environmental impact; 40% of the total hot rolled steel in the marketplace is from recycling. In this article, we will go into the process, benefits, and challenges faced during hot-rolled carbon steel recycling.
What is Hot Rolled Carbon Steel?
Manufacturing hot-rolled carbon steel is quite simple: the raw steel, SLAB/BILLET/INGOT, is heated to a very high temperature—up to 926°C–1400 °C—until it becomes molten, thus attaining its capacity to easily be rolled out into various steels. At such high-temperature rolling, the processing becomes easy on steel, manufacturing, for instance, H-beams, I-Beams, TMT Bars, and Plates used for heavy-duty manufacturing in construction-related ventures. It is called so because it contains carbon, up to 2%, hence giving this component high strength with high hardness properties.

Some characteristics of hot rolled carbon steel include:
Strength and Durability: Suitable for structural application.
Cost-Effectiveness: It’s easier and less expensive to produce than other types of steel.
Versatility: Can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes, therefore applicable in different industries.
Importance of Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Recycling
Hot rolled carbon steel recycling offers important benefits for both the environment and the economy:
Natural Resources Conservation:
Hot rolled carbon steel recycling is the conservation of natural resources. Mining iron ore and coal—for the extraction of these two materials—is very energy-intensive and environment-destructive. Recycling steel saves the need to mine raw materials, hence reduces the strain on natural resources, and saves forests and ecosystems from further damage caused by mining and extractions for the sake of environmental sustainability.
To reduce energy consumption:
Hot rolled carbon steel recycling saves 60-70% of energy compared to traditional steel production. To manufacture virgin steel, furnaces need to be heated to extreme temperatures, thus hugely consuming energy. Melting of recycle steel, however requires comparatively less amount of energy. Because of this energy efficiency, recycling significantly lowers carbon emissions and promotes eco-friendly manufacturing.
Waste Management:
Hot rolled carbon steel recycling converts the steel scrap into useful products, not going into landfill. Waste of steel through dumping in landfills is sheer wastage of space and causing long-term environmental problems. Recycling provides the sustainable way to manage the waste generated and converts it into productive material.
Cost Savings:
It costs much less to produce the recycled steel than to produce virgin steel. Since the industries are able to decrease the overall cost of production owing to the decrease in demand for raw materials and energy, cost efficiency makes industries economical and competitive, which also maximizes long-term profitability.
Reduction in Environmental Impact:
Hot rolled carbon steel recycling reduces greenhouse gas emissions and industrial waste. The carbon footprint of recycling is considerably lower than that of virgin steel production. This process impacts the environment in a positive way and contributes to the battle against the effects of climate change. Recycling also reduces water pollution and air pollution.
Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Recycling Process
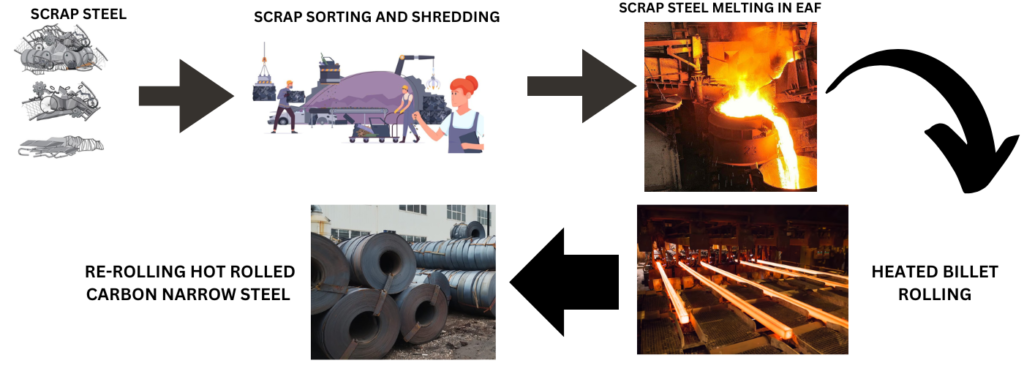
The recycling of hot rolled carbon steel involves several key steps:
Step 1: Scrap Collection
The collection of steel scrap is a first action in the recycling process. This scrap can come from a variety of sources, including tear-down buildings, discarded automobiles, non-working machinery, and materials left over from manufacturing processes. Specialized companies and scrapyards are involved in collecting and sorting steel scrap based on quality and type.
Step 2: Sorting and Preparation
After collection, the steel is sorted. Sorting is important to ensure that only clean carbon steel enters the recycling process. The different types of steel and metals get separated so material purity is preserved. Non-ferrous metals, plastics, and contaminants get removed through magnetic separation and by hand inspection.
Step 3: Shredding and Melting
After sorting is completed, the steel scrap is fed into shredders and broken into small pieces. These small pieces help in easy handling as well as fast melting. The shredded steel is then fed into electric arc furnaces (EAF) and melted at a high temperature. Melting of scrap in EAF consumes far less energy as compared to the production of new steel.
Step 4: Refining and Alloying
At this stage, impurities like sulphur, phosphorus, and carbon are removed to maintain the quality of the recycled steel. Alloying elements may also be added to meet specific requirements. This refining process makes the recycled steel suitable for new products.
Step 5: Casting and Rolling
From there, it undergoes a series of processes: first, the molten steel is cast into slabs or billets; second, these slabs or billets are rolled into hot-rolled carbon steel products, beams, sheets, or bars ready for different applications.
Step 6: Distribution and Reuse
Recycled steel products are then transported to various industries, which again transform them for use in construction, manufacturing, automotive, and many more. High-quality, low-cost, environment-friendly recycled steel helps industries satisfy their material needs.

Benefits of Recycling Hot Rolled Carbon Steel
The benefits of hot rolled carbon steel recycling are many, which include:
Natural resource conservation: It reduces demand for raw materials such as iron ore and coal, thus helping in the preservation of natural resources and a reduction in the environmental impact of mining.
Energy efficiency: The recycling process involves less energy compared to the production of virgin steel, therefore saving energy resources and pollution.
Cost Savings: The cost associated with producing steel from scrap is lower, as it requires less raw material and energy; hence, it is economical for industries.
Waste Reduction: It saves steel scrap from landfills and consequently reduces demand for waste generation and landfill space.
Promotes Circular Economy: Steel recycling boosts the idea of a circular economy where materials are meant to be reused and waste is minimized to the barest level, or even eliminated.
Job Creation: The industry associated with recycling generates new employment opportunities, therefore leading to economic growth based on social benefits.
Industrial Applications: The recycled steel from this industry will provide industrial sectors like construction, automotive, and machinery with materials that are reliable in terms of cost.
Global Sustainability Goals: Hot rolled carbon steel recycling supports sustainable practices and helps to achieve global environmental objectives.
Issues in Recycling of Hot Rolled Carbon Steel
Sorting Complexity: The recycling of steel scrap involves the segregation of the different grades of steel that are mixed with other materials like plastic, wood, and aluminum. If the sorting is not done precisely, the quality of the recycled steel gets degraded substantially. Advanced technologies in sorting, such as magnetic separation and AI-driven methods, do help much but are time-consuming and costly. Manual sorting is also possible but comes with the risk of human error, impacting efficiency.
Contamination Issues: Such impurities in steel scrap, like oil, grease, paints, and coatings, increase contamination. These impurities make the refining process complex and costly. If the contamination is not effectively removed, it affects the properties of the recycled steel—reliability is reduced in the end product. This requires special cleaning and refining techniques, which increase operational costs and slow down the process.
Energy and Resource Demand: Hot rolled carbon steel recycling is energy efficient, high temperature furnaces are needed in both melting and refining processes. Furnaces require energy to operate thus increasing the costs of operation. In addition, refining requires chemical and other related resources that cause environmental and financial impacts.
Quality Control: It can be challenging to ensure the quality of recycled steel because the source and composition of scrap varies. Bad quality scrap may lead to low strength and poor durability in the finished product. This needs specialized testing and refining methods, which increases the cost and reduces the speed of the process.
Technological Limitations: In hot rolled carbon steel recycling, there is a need for advanced technologies that can handle contamination, sorting, and refining issues in an effective way. Most of these technologies are inaccessible in developing countries, hence reducing efficiency in recycling. Besides, upgrading technology is an expensive process, which small-scale recyclers cannot afford.
Economic Challenges: High up-front costs: There is the requirement for modern machines, logistics, and specialized labour, increasing the difficulty for small-scale recyclers to handle, hence making them less competitive. Low-margin operations also make it difficult to reach long-term profitability.
Environmental Concerns: Steel recycling involves energy consumption and emissions, which may affect the environment. The melting and refining processes give off toxic gases and residues, which are harmful if not disposed of properly. This calls for very strict environmental regulations and highly developed pollution control systems, which are expensive to put in place.
Innovations in Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Recycling
Innovations and new technologies are making hot rolled carbon steel recycling increasingly efficient and environmentally friendly.
Automated Sorting: Advanced machinery, utilizing sensors and artificial intelligence, can sort metals with great accuracy, therefore increasing efficiency while reducing contamination.
Electric Arc Furnace Technology: New developments in EAF technology enable faster, more energy-efficient melting to lower costs and emissions.
Recyclable-friendly alloys: Alloy formulations with less contamination to recycle and with less problems related to contamination.
Sustainable Transportation: Electric and hybrid vehicles used in scrap collection and transportation reduce the carbon footprint of the recycling operation.
The Future of Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Recycling
With increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials, there is immense potential for the recycling of steel. Companies use recycled steel to reduce their environmental footprint while, at the same time, strict environmental regulations by governments encourage the steel industry to step up their recycling efforts.
Hot rolled carbon steel recycling is one of the basic components of the circular economy, helping industries to reduce waste, cut costs, and have a positive impact on the environment. With new innovations continuing, hot rolled carbon steel recycling is going to become more efficient and open ways toward a greener future.
Conclusion
Recycling of hot-rolled carbon steel saves resources and helps the environment by supporting the sustainable economy. Its efficient recycling methodologies convert scrap into valuable material that would otherwise go into landfill, further prolonging the life of this steel. Several challenges exist, like contamination or issues relating to quality control; still, technology improvement keeps on making the process of steel recycling more viable and sustainable, and as industry and societies turn greener.




Pingback: WHY IS CHINESE STEEL SO LOW COST? LETS FINDOUT